THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO HORMONE OPTIMIZATION: NATURAL METHODS FOR MEN & WOMEN IN 2025
Evidence-Based Strategies for Optimal Health and Vitality
In 2025, hormone imbalance has reached epidemic proportions, affecting over 80% of adults over 35 years old in the United States. Recent studies reveal that environmental toxins, chronic stress, poor sleep quality, and modern lifestyle factors have created a perfect storm for hormonal disruption. While traditional hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has dominated the medical landscape for decades, a growing body of research shows that natural hormone optimization offers safer, more sustainable solutions for restoring hormonal balance.
The alarming statistics speak for themselves: nearly 40% of women entering perimenopause experience debilitating symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life, while testosterone levels in men have declined by 1-2% annually over the past four decades. More concerning is that conventional medicine’s approach of simply replacing hormones often addresses symptoms without targeting root causes, potentially leading to dependency and long-term health risks.
This comprehensive guide introduces a revolutionary approach to hormone optimization that goes beyond traditional replacement therapy. You’ll discover evidence-based natural methods that support your body’s innate ability to produce, balance, and optimize hormones naturally. Unlike quick fixes that merely mask symptoms, these strategies address the underlying factors that disrupt hormonal harmony.
Whether you’re a woman navigating perimenopause, a man experiencing declining testosterone, or simply someone seeking to optimize their hormonal health for longevity and vitality, this guide provides the tools and knowledge needed to take control of your hormonal destiny naturally and safely.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Hormone Optimization vs. Hormone Replacement
1.1 What is Hormone Optimization?
Hormone optimization represents a paradigm shift from the traditional medical model of hormone replacement therapy. Rather than simply replacing hormones that have declined, hormone optimization focuses on supporting your body’s natural ability to produce, balance, and utilize hormones effectively. This approach recognizes that hormones function as an interconnected symphony, where each hormone influences and is influenced by others in complex feedback loops.
Core Principles of Hormone Optimization:
- Address root causes rather than just symptoms
- Support natural hormone production mechanisms
- Consider the interconnected nature of the endocrine system
- Preventive approach vs. reactive treatment
The core principle of hormone optimization lies in addressing the root causes of hormonal imbalance rather than merely treating symptoms. This preventive approach considers factors such as nutrition, sleep quality, stress management, exercise, environmental toxin exposure, and gut health as fundamental drivers of hormonal health.
1.2 Hormone Optimization vs. Traditional HRT
Recent Research (JAMA 2024): While HRT can provide rapid symptom relief, it often creates dependency and may carry long-term risks including increased cardiovascular events and certain cancers when used inappropriately or without proper monitoring.
The fundamental difference between hormone optimization and traditional hormone replacement therapy (HRT) lies in their underlying philosophies and methodologies. Traditional HRT typically involves prescribing synthetic or bioidentical hormones to replace what the body is no longer producing in adequate amounts.
Key Differences:
Traditional HRT
- Adds external hormones
- May create dependency
- Focuses on isolated hormones
- Potential long-term risks
- Symptom-focused approach
Hormone Optimization
- Supports natural production
- Addresses root causes
- Systems-based approach
- Minimal side effects
- Prevention-focused strategy
1.3 The 2025 Approach to Hormone Health
The landscape of hormone health has evolved dramatically in 2025, with breakthrough discoveries in personalized medicine, biomarker testing, and functional medicine approaches transforming how we understand and address hormonal imbalances. Advanced testing now allows for precise measurement of hormone metabolites, providing insights into how effectively the body is producing, utilizing, and clearing hormones.
2025 Breakthrough Developments:
- Environmental Assessment: Recognition of 300+ endocrine disruptors in everyday products
- Functional Medicine Integration: Systems-based approach to hormone health
- Advanced Biomarkers: Hormone receptor sensitivity and genetic testing
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time tracking of hormonal fluctuations
- Personalized Protocols: Tailored to individual genetic profiles
2. The Science Behind Hormone Optimization

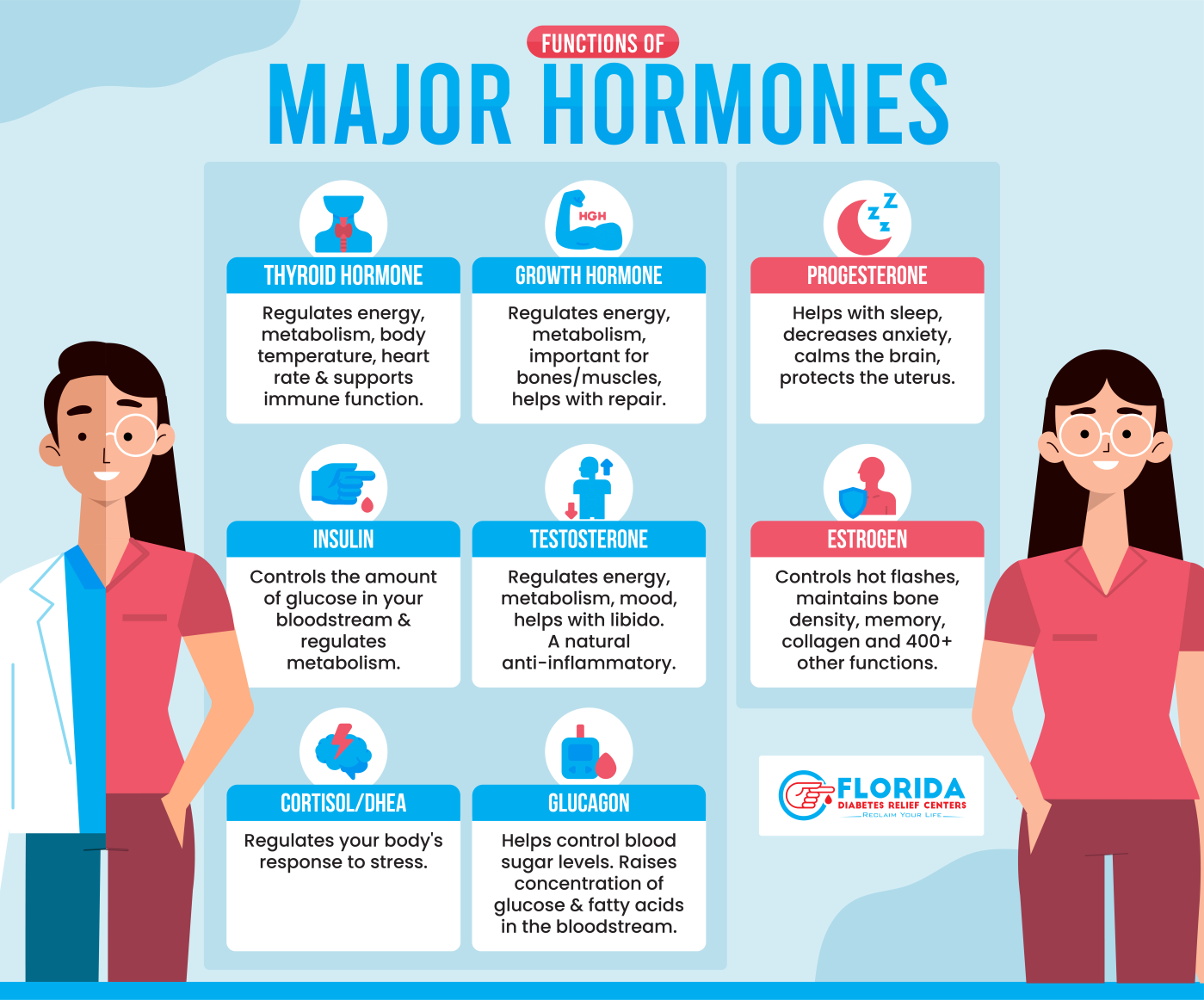
2.1 Key Hormones and Their Functions
Understanding the major players in your hormonal orchestra is essential for effective optimization. Each hormone serves specific functions while participating in complex feedback loops that maintain overall hormonal harmony.
Estrogen: The Master Regulator
Estrogen, primarily produced in the ovaries, serves functions far beyond reproduction. Research from Harvard Medical School (2024) demonstrates that estrogen receptors are found throughout the body, influencing:
- • Cardiovascular health and cholesterol metabolism
- • Bone density and calcium absorption
- • Cognitive function and memory
- • Mood regulation and neurotransmitter balance
- • Insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism
Progesterone: The Calming Influence
Often called the “happiness hormone,” progesterone provides natural anxiety relief and balances estrogen’s effects:
- • GABA-like effects promoting calm and sleep
- • Balances estrogen to prevent dominance
- • Supports healthy pregnancy and fertility
- • Regulates menstrual cycles in women
- • Serves as testosterone precursor in men
Testosterone: Beyond Libido
Research published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology (2024) reveals testosterone’s crucial roles for both sexes:
- • Muscle mass and bone density maintenance
- • Cognitive function and mental clarity
- • Cardiovascular health protection
- • Energy production and motivation
- • Sexual function and libido
Cortisol: The Double-Edged Sword
Essential for survival but destructive when chronically elevated. Stanford University (2024) found 73% of adults have abnormal cortisol patterns:
- • Should be high in morning, low at night
- • Chronic elevation causes inflammation
- • Disrupts other hormone production
- • Affects immune system function
- • Contributes to insulin resistance
Additional Key Hormones:
Thyroid Hormones (T3/T4)
Regulate metabolism, energy production, and temperature. Many have adequate T4 but poor T3 conversion.
Insulin
Master metabolic hormone. Resistance affects 50% of adults and disrupts sex hormone production.
Growth Hormone
Anti-aging hormone released during deep sleep. Supports tissue repair and fat metabolism.
2.2 The Hormone Symphony
Hormones function as an intricate symphony, where each hormone’s “note” contributes to overall hormonal harmony. This interconnected system means that imbalances in one hormone inevitably affect others, creating cascading effects throughout the body.
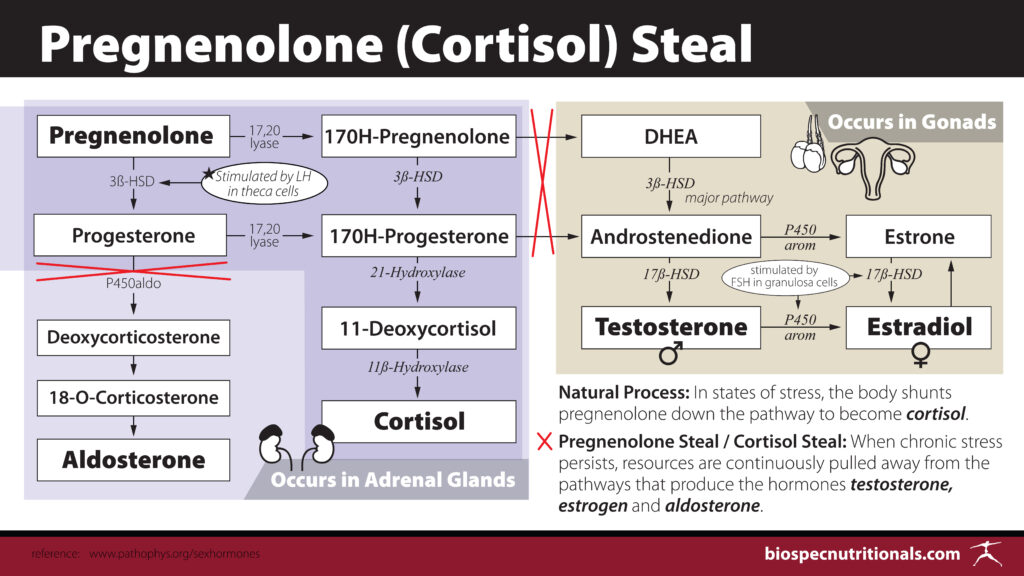
The HPA Axis: Your Hormonal Conductor
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis serves as the conductor of this orchestra, responding to internal and external stressors by modulating hormone production throughout the body. When the HPA axis becomes dysregulated—often due to chronic stress—it disrupts the delicate balance of sex hormones, thyroid hormones, and metabolic hormones.
Example: The Stress-Hormone Cascade
Chronic stress → Elevated cortisol → Inhibited testosterone/progesterone → Promoted estrogen dominance → Impaired thyroid conversion → Increased insulin resistance → Further hormonal disruption
2.3 Factors That Disrupt Hormone Balance
The modern world presents unprecedented challenges to hormonal health. Understanding these disruptors is essential for developing effective optimization strategies.
Environmental Toxins
A 2024 Environmental Health Perspectives study identified 300+ endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs):
- • BPA, phthalates, parabens in everyday products
- • Found in 95% of Americans tested
- • Accumulate in fat tissue for years
- • Effects at extremely low doses
- • Particularly dangerous during development
Chronic Stress
Modern psychological stress creates persistent HPA axis activation:
- • Elevates cortisol chronically
- • Suppresses sex hormone production
- • Reduces testosterone by 20-30%
- • Impairs insulin sensitivity
- • Disrupts sleep and recovery
Poor Nutrition
Standard American Diet creates hormonal chaos:
- • Processed foods cause insulin resistance
- • High sugar disrupts hormone production
- • Industrial oils promote inflammation
- • Nutrient deficiencies impair synthesis
- • Lack of hormone-building nutrients
Sleep Disruption
Modern lifestyle disrupts natural hormone rhythms:
- • Growth hormone released during deep sleep
- • Blue light suppresses melatonin
- • Poor sleep reduces testosterone 10-15%
- • Disrupts circadian hormone patterns
- • Shift work increases hormone disorders
3. Signs You Need Hormone Optimization
3.1 Universal Signs of Hormone Imbalance
Recognizing the early warning signs of hormone imbalance is crucial for timely intervention. Many symptoms are subtle initially but progressively worsen without proper attention.
Mayo Clinic Research (2024): 85% of individuals with hormone imbalances report significant fatigue as their primary concern, distinguishing it from normal tiredness by its persistence despite adequate rest.
Persistent Fatigue
Deep exhaustion that doesn’t improve with rest, often with afternoon energy crashes
Unexplained Weight Gain
Weight gain around midsection despite maintaining previous eating and exercise habits
Mood Swings
Increased irritability over minor issues, unexpected emotional outbursts
Sleep Disturbances
Difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, or early morning waking
Brain Fog
Difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, reduced mental clarity
Temperature Issues
Hot flashes, night sweats, or feeling cold when others are comfortable
3.2 Women-Specific Symptoms
Women experience unique hormonal challenges throughout their lives, from puberty through menopause and beyond. Understanding these gender-specific signs can help identify when hormone optimization is needed.
Menstrual & Reproductive Signs
- Irregular or painful periods (cycles <24 or >35 days)
- Severe PMS or PMDD symptoms
- Heavy bleeding or severe cramping
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness and low libido
Physical & Emotional Signs
- Hair loss or thinning, especially at crown
- Adult-onset acne, particularly jawline
- Skin changes and loss of elasticity
- Breast tenderness and swelling
- Anxiety and mood swings
3.3 Men-Specific Symptoms
Men experience more gradual hormonal changes than women, but these changes can significantly impact health, vitality, and quality of life. Recognizing male-specific symptoms of hormone imbalance is crucial for early intervention.
Sexual & Physical Health
- Low libido and erectile dysfunction
- Loss of morning erections
- Muscle loss despite continued exercise
- Increased belly fat accumulation
- Reduced recovery from exercise
Mental & Emotional Health
- Decreased motivation and drive
- Mood changes and irritability
- Depression and emotional flatness
- Reduced competitive spirit
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
3.4 Age-Related Hormone Changes

Women’s Hormonal Timeline
Perimenopause (40s-early 50s)
Hormone fluctuations, irregular cycles, early symptoms
Menopause (avg. age 51)
12 months without menstruation, dramatic hormone decline
Post-menopause
Increased risks for osteoporosis, heart disease, cognitive decline
Men’s Hormonal Timeline
Age 30+
Testosterone begins declining 1-2% annually
Age 40+
More noticeable symptoms, growth hormone decline
Age 50+
Significant impact on energy, body composition, vitality
When to Start Paying Attention
The optimal time to begin monitoring and optimizing hormones is before symptoms become severe. For women, this typically means paying attention to cycle changes and symptoms beginning in their mid-30s. For men, baseline testing in their 30s can provide valuable reference points for future comparison. Preventive hormone optimization is more effective than waiting until symptoms significantly impact quality of life.
4. Hormone Optimization for Women

4.1 Women’s Hormone Optimization Over 40
North American Menopause Society (2024): Women who proactively address hormonal changes in their 40s experience 60% fewer severe menopausal symptoms and maintain better cognitive function, bone density, and cardiovascular health.
Women over 40 face unique hormonal challenges as they transition through perimenopause and beyond. This decade often marks the beginning of significant hormonal fluctuations that can dramatically impact quality of life, energy levels, and long-term health.
Perimenopause: Understanding the Transition
Perimenopause typically begins in the early to mid-40s, though some women notice changes as early as their late 30s. During this phase, estrogen and progesterone levels fluctuate unpredictably, creating a hormonal rollercoaster that can last several years.
Key Perimenopause Characteristics:
- • Unpredictable hormone swings
- • Irregular menstrual cycles
- • Varying symptom severity month to month
- • Hot flashes and night sweats
- • Mood changes and irritability
- • Sleep disturbances
- • Changes in sexual function
- • Weight gain tendency
Natural Management Strategies
Adrenal Support
Supporting adrenal function helps maintain hormone production as ovarian function declines.
- • Adaptogenic herbs (ashwagandha, rhodiola)
- • B-vitamin complex for stress support
- • Magnesium for relaxation
- • Regular sleep schedule
Liver Detoxification
Efficient hormone clearance prevents accumulation and imbalances.
- • Cruciferous vegetables daily
- • Milk thistle supplementation
- • Adequate hydration
- • Fiber-rich foods
4.2 Natural Testosterone Therapy for Women
The importance of testosterone for women’s health has been significantly underrecognized in conventional medicine. Women produce testosterone in their ovaries, adrenal glands, and peripheral tissues, and while they require much lower levels than men, this hormone is crucial for energy, libido, muscle mass, bone density, and overall vitality.
Harvard Medical School (2024): Women with optimal testosterone levels maintain better cognitive function, physical strength, and sexual satisfaction throughout menopause and beyond.
Why Women Need Testosterone
- Muscle Mass: Supports protein synthesis and prevents age-related muscle loss
- Cognitive Function: Enhances memory, spatial reasoning, and mental clarity
- Bone Health: Directly stimulates bone formation and prevents osteoporosis
- Mood & Motivation: Supports confidence, assertiveness, and drive
Natural Support Methods
- Resistance Training: 25-30% higher levels in women who strength train regularly
- Adequate Protein: 0.8-1.2g per kg body weight daily for hormone synthesis
- Key Nutrients: Zinc, magnesium, vitamin D, healthy fats
- Quality Sleep: Overnight testosterone production during deep sleep
4.3 PCOS and Hormone Balance
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age and represents one of the most common hormonal disorders affecting women. Recent research has revolutionized our understanding of PCOS, revealing that insulin resistance is the underlying driver in most cases.
Understanding the PCOS-Insulin Connection
Insulin resistance is present in 65-70% of women with PCOS, regardless of body weight. When cells become resistant to insulin’s effects, the pancreas produces increasingly higher levels of insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
The PCOS Cascade:
Insulin Resistance → High Insulin Levels → Increased Androgen Production → Reduced SHBG → Higher Free Androgens → PCOS Symptoms (irregular cycles, acne, hair growth, weight gain)
Dietary Interventions
Low-Glycemic Approach
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024): 40% improvement in insulin sensitivity, 35% reduction in androgens within 12 weeks
Key Strategies
- • Protein with every meal for blood sugar stability
- • High-fiber vegetables to slow glucose absorption
- • Avoid processed foods and added sugars
- • Anti-inflammatory foods (omega-3s, turmeric)
- • Intermittent fasting for insulin sensitivity
Lifestyle Modifications
Exercise Protocol
- • HIIT for improved insulin sensitivity
- • Resistance training for muscle building
- • Balance intensity to avoid excess cortisol
- • 150+ minutes moderate activity weekly
Stress Management
- • Critical for cortisol balance
- • Meditation and mindfulness practices
- • Adequate sleep (7-9 hours nightly)
- • Support systems and counseling
Evidence-Based Supplements for PCOS
Inositol
Myo-inositol + D-chiro-inositol improves insulin sensitivity and reduces androgens
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Reduces inflammation and improves insulin sensitivity
Spearmint Tea
Anti-androgenic properties, reduces free testosterone
4.4 Thyroid Optimization for Women
Thyroid disorders affect women five to eight times more frequently than men, with many women struggling with undiagnosed or inadequately treated thyroid dysfunction. The thyroid gland serves as the body’s metabolic control center, influencing energy production, temperature regulation, heart rate, and virtually every cellular process.
Hashimoto’s and Autoimmune Thyroid Conditions
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis affects up to 10% of women and is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in developed countries. This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks thyroid tissue, gradually destroying the gland’s ability to produce hormones.
European Journal of Endocrinology (2024): 75% of women with Hashimoto’s who followed a strict gluten-free diet for six months showed significant reductions in thyroid antibody levels.
Natural Thyroid Support
Key Nutrients
- • Iodine: Essential but must be balanced (seaweeds)
- • Selenium: 2-3 Brazil nuts daily for antibody reduction
- • Tyrosine: Amino acid backbone of thyroid hormones
- • Iron: Required for hormone production (test first)
- • Zinc: Supports T4 to T3 conversion
Thyroid-Supporting Foods
- • Sea vegetables (dulse, kelp) for natural iodine
- • Cooked cruciferous vegetables (avoid raw if hypothyroid)
- • Anti-inflammatory foods (omega-3s, turmeric)
- • Liver-supporting foods for T4→T3 conversion
Lifestyle Factors
Foods to Limit
- • Gluten (especially with Hashimoto’s)
- • Soy products (can interfere with thyroid function)
- • Excessive raw cruciferous vegetables
- • Coffee within 1 hour of thyroid medication
Stress & Sleep
- • Chronic stress impairs T4→T3 conversion
- • Prioritize 7-9 hours quality sleep
- • Manage cortisol through stress reduction
- • Support adrenal function
5. Hormone Optimization for Men
5.1 Male Hormone Optimization Over 40
American Urological Association (2024): Testosterone levels in 40-year-old men today are 20-30% lower than those of 40-year-old men from previous generations, suggesting modern lifestyle factors are accelerating age-related hormone decline.
Men entering their fifth decade face a hormonal landscape dramatically different from their younger years. Unlike women, who experience relatively sudden hormonal changes during menopause, men undergo a gradual but relentless decline in key hormones, particularly testosterone and growth hormone.
Understanding Andropause
Andropause describes the gradual decline in testosterone and other hormones that affects most men as they age. This decline affects multiple aspects of health and vitality, but it’s not inevitable or irreversible.
Hormone Decline Timeline
- • Age 30: Testosterone begins 1-2% annual decline
- • Age 40: More noticeable symptoms emerge
- • After 40: Growth hormone drops 14% per decade
- • Age 50+: Significant impact on vitality
Affected Functions
- • Muscle mass and bone density
- • Cognitive function and mood
- • Sexual health and libido
- • Cardiovascular function
- • Energy and recovery
Natural Optimization Strategies
Sleep Optimization
Testosterone produced during deep sleep, peaks in early morning
- • 7+ hours quality sleep nightly
- • Cool, dark environment (65-68°F)
- • Consistent sleep schedule
- • No electronics 1 hour before bed
Stress Management
Chronic stress reduces testosterone by 20-30%
- • Regular meditation practice
- • Deep breathing exercises
- • Time in nature
- • Physical stress outlets
Body Composition
Excess fat contains aromatase enzyme converting testosterone to estrogen
- • Maintain 10-15% body fat
- • Avoid extreme dieting
- • Preserve muscle mass
- • Gradual, sustainable approach
5.2 Natural Testosterone Optimization
Testosterone optimization for men requires a comprehensive approach that addresses all factors influencing production, utilization, and clearance of this crucial hormone. Natural optimization methods work synergistically to support optimal testosterone levels while improving overall health and vitality.
Exercise Protocols for Hormone Optimization
Exercise is one of the most powerful tools for natural testosterone optimization, but the type, intensity, and frequency significantly impact hormonal responses.
Resistance Training Foundation
- Compound Movements: Squats, deadlifts, bench press, rows
- Optimal Range: 6-10 reps at 75-85% 1RM
- Rest Periods: 60-90 seconds between sets
- Frequency: 3-4 sessions per week
- Progressive Overload: Gradual increases in weight/reps
HIIT for Hormone Boost
- Protocol: 30 sec high intensity / 90 sec recovery
- Duration: 15-20 minutes total
- Frequency: 2-3 sessions per week
- Recovery: Minimum 1 day between sessions
- Avoid: Excessive endurance exercise
Nutrition for Testosterone Production
Healthy Fats (25-35% calories)
- • Saturated: Grass-fed beef, eggs, coconut oil
- • Monounsaturated: Olive oil, avocados, nuts
- • Omega-3: Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts
Protein (1.2-1.6g/kg body weight)
- • Complete amino acid profiles
- • Grass-fed meat and poultry
- • Wild-caught fish
- • Pastured eggs
Complex Carbohydrates
- • Around exercise for cortisol management
- • Sweet potatoes, quinoa, oats
- • Avoid very low-carb long-term
- • Support insulin sensitivity
5.3 Managing Low Testosterone Naturally
For men with clinically low testosterone levels, natural optimization approaches can often restore healthy levels without pharmaceutical intervention. Understanding the root causes and addressing them systematically provides the best opportunity for natural restoration.
Identifying Root Causes of Low T
Environmental Factors
- Endocrine Disruptors: BPA, phthalates, parabens in plastics and personal care
- Pesticides: Residues on conventionally grown produce
- Heavy Metals: Lead, mercury, aluminum exposure
- EMF Exposure: Chronic electromagnetic field exposure
Metabolic Issues
- Insulin Resistance: Affects 50% of men over 40
- Chronic Inflammation: From poor diet, stress, toxins
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Zinc, vitamin D, magnesium, B-vitamins
- Poor Gut Health: Dysbiosis affecting hormone metabolism
Natural Therapies and Interventions
Targeted Foods
- • Pomegranate Juice: 24% T increase in 60 days
- • Cruciferous Vegetables: Support estrogen metabolism
- • Fermented Foods: Gut health for hormone balance
- • Oysters: Highest zinc content of any food
Herbal Support
- • Ashwagandha: 15-25% T increase in studies
- • Tongkat Ali: Increases free testosterone
- • Fenugreek: Inhibits testosterone conversion
- • D-Aspartic Acid: Supports LH production
Lifestyle Interventions
- • Cold Therapy: Ice baths, cold showers
- • Sauna Therapy: Heat shock proteins, detox
- • Intermittent Fasting: Improves insulin sensitivity
- • Sun Exposure: Natural vitamin D production
5.4 Prostate Health and Hormone Balance
Prostate health becomes an increasingly important consideration for men as they age, and hormonal balance plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal prostate function. Understanding the relationship between hormones and prostate health allows men to make informed decisions about hormone optimization.
DHT and Prostate Health Considerations
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a potent androgen derived from testosterone through 5-alpha reductase enzyme action. While necessary for normal prostate function, excessive levels may contribute to prostate enlargement.
Natural DHT Management
- • Green Tea: EGCG inhibits 5-alpha reductase
- • Pumpkin Seeds: Zinc and natural 5AR inhibition
- • Saw Palmetto: May help maintain healthy prostate size
- • Nettle Root: Supports healthy DHT metabolism
Prostate-Supporting Foods
- • Lycopene: Cooked tomatoes, watermelon
- • Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower
- • Pomegranate: Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory
- • Fatty Fish: Omega-3s for inflammation
Long-term Prostate Health Strategy
Maintaining optimal hormone balance throughout life may be one of the most important factors for long-term prostate health, including managing insulin resistance, estrogen balance, and inflammation.
- • Regular Monitoring: PSA tests and digital exams for men 40+
- • Insulin Sensitivity: Maintain healthy glucose metabolism
- • Estrogen Balance: Support healthy estrogen-to-testosterone ratios
- • Inflammation Control: Anti-inflammatory diet and lifestyle
6. Natural Methods for Hormone Balance

6.1 Hormone Balancing Foods
The foods we consume daily provide the building blocks for hormone production while directly influencing hormonal activity throughout the body. Modern research has revealed that food acts as more than just fuel—it functions as information that directly communicates with our hormonal systems.
Phytoestrogen-Rich Foods and Their Benefits
Phytoestrogens are plant compounds that can mimic or modulate estrogen activity in the body. These compounds help balance hormones, particularly during perimenopause and menopause when estrogen levels fluctuate dramatically.
Flaxseeds
Richest source of lignans (phytoestrogens)
- • 2 tablespoons ground daily
- • Improves estrogen metabolism
- • Provides omega-3 fatty acids
- • Must be ground for absorption
Legumes
Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
- • Contain isoflavones
- • Help modulate estrogen activity
- • Beneficial for estrogen dominance
- • Provide fiber and protein
Fermented Soy
Tempeh, miso, natto
- • More bioavailable isoflavones
- • Fermentation improves absorption
- • Choose organic, non-GMO
- • Moderate amounts only
Healthy Fats for Hormone Production
Dietary fats serve as the building blocks for all steroid hormones. Without adequate healthy fats, the body cannot produce optimal amounts of crucial hormones.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- • Cold-water fish: Salmon, sardines, mackerel
- • Plant sources: Walnuts, chia, hemp seeds
- • Algae supplements: For vegetarians/vegans
- • Benefits: Reduce inflammation, support brain function
Monounsaturated Fats
- • Extra virgin olive oil: Supports testosterone in men
- • Avocados: Rich in healthy fats and fiber
- • Nuts and seeds: Almonds, pistachios
- • Benefits: Heart health, hormone synthesis
Quality Saturated Fats
- • Grass-fed beef: Contains CLA and vitamin K2
- • Pastured eggs: Complete amino acid profile
- • Coconut oil: Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs)
- • Benefits: Essential for hormone production
Foods to Avoid for Optimal Hormone Health
Hormone Disruptors
- Ultra-processed foods: High in refined sugars, industrial oils, additives
- Industrial seed oils: Soybean, corn, cottonseed, canola
- High-fructose corn syrup: Promotes insulin resistance
- Excessive alcohol: Disrupts sleep, elevates cortisol
Better Alternatives
- Whole foods: Minimize processing and additives
- Traditional fats: Olive oil, coconut oil, grass-fed butter
- Natural sweeteners: Stevia, monk fruit, raw honey (moderation)
- Moderate alcohol: Organic wine, occasional consumption
6.2 Adaptogenic Herbs for Hormone Balance
Adaptogenic herbs represent one of the most promising natural approaches to hormone optimization. These unique plants help the body adapt to stress while supporting optimal endocrine function through normalizing and balancing multiple systems simultaneously.
To qualify as an adaptogen, a substance must be non-toxic, help the body cope with stress, and have a normalizing effect on physiological functions—increasing function when it’s too low and decreasing it when it’s too high.
Ashwagandha
Research: 27% reduction in morning cortisol levels, 10-22% increase in testosterone (men)
- • Reduces stress and cortisol
- • Improves sleep quality
- • Supports testosterone in men
- • Enhances stress resilience
Maca Root
Research: Improves sexual function and energy without changing hormone levels directly
- • Enhances libido and sexual function
- • Improves energy and stamina
- • Balances overall endocrine system
- • Reduces menopausal symptoms
Holy Basil (Tulsi)
Research: Normalizes cortisol rhythms, improves stress adaptation and sleep quality
- • Normalizes cortisol patterns
- • Improves blood sugar regulation
- • Reduces chronic inflammation
- • Enhances spiritual well-being
Rhodiola Rosea
Research: Reduces mental fatigue, improves concentration and mood under stress
- • Enhances mental performance
- • Reduces fatigue and burnout
- • Supports thyroid function
- • Improves exercise performance
Tongkat Ali
Research: 15-37% increase in testosterone levels, improved sexual function in men
- • Increases free testosterone
- • Enhances sexual function
- • Improves muscle mass and strength
- • Boosts energy and vitality
Schisandra Berry
Research: Supports liver detoxification and protects against environmental stress
- • Enhances liver detoxification
- • Protects against environmental toxins
- • Improves mental clarity
- • Supports healthy aging
6.3 Essential Nutrients for Hormone Production
Optimal hormone production requires adequate levels of specific vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that serve as cofactors in hormone synthesis and metabolism. Even with perfect lifestyle habits, nutrient deficiencies can significantly impair hormonal function.
Vitamin D
Functions like a hormone with receptors throughout the body
- • 20-30% higher testosterone in men
- • Supports immune function
- • Essential for bone health
- • Reduces inflammation
Dosage: 1000-4000 IU daily
Zinc
Cofactor in 300+ enzymatic reactions including testosterone synthesis
- • 20-50% T increase if deficient
- • Immune system support
- • Wound healing
- • Reproductive health
Dosage: 15-30mg daily (with copper)
Magnesium
Involved in 600+ enzymatic reactions, crucial for stress and sleep
- • Regulates HPA axis
- • Supports deep sleep
- • Reduces cortisol
- • GABA production
Dosage: 400-600mg daily
B-Vitamins
Complex of 8 vitamins working synergistically for energy and mood
- • B6: Hormone metabolism, PMS relief
- • B12: Energy, methylation
- • Folate: Methylation, mood
- • B5: Adrenal support
Dosage: B-complex daily
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Inflammation Control
Why Omega-3s Are Critical
The typical Western diet provides omega-6 to omega-3 ratios of 15-20:1, creating chronic inflammation that disrupts hormone production. The optimal ratio is 2-4:1.
- • EPA: Potent anti-inflammatory effects
- • DHA: Brain health and neurotransmitter support
- • Benefits: Improve insulin sensitivity, reduce cortisol, support testosterone
Best Sources & Dosage
- Cold-water fish: Salmon, sardines, mackerel, anchovies
- Quality supplements: Molecularly distilled fish oil or algae-based
- Plant sources: Limited conversion from ALA (flax, chia, walnuts)
- Optimal dosage: 1-3 grams combined EPA/DHA daily
- Third-party testing: Ensures purity and potency
6.4 Detoxification and Hormone Health
The body’s ability to metabolize and eliminate hormones is just as important as its ability to produce them. When detoxification pathways become overwhelmed or impaired, hormones can accumulate to problematic levels or be converted to harmful metabolites.
Supporting Liver Function for Hormone Metabolism
The liver serves as the body’s primary detoxification organ and plays crucial roles in hormone metabolism. Most hormones must pass through the liver for processing and elimination through two main phases of detoxification.
Phase I Detoxification
Cytochrome P450 enzymes begin breaking down hormones and toxins
- • Support with: B-vitamins, antioxidants
- • Foods: Beets, carrots, green tea
- • Herbs: Milk thistle, turmeric
Phase II Detoxification
Conjugation reactions make compounds water-soluble for elimination
- • Support with: Sulfur compounds, amino acids
- • Foods: Cruciferous vegetables, garlic, onions
- • Nutrients: Glutathione, NAC, glycine
Reducing Endocrine Disruptor Exposure
Environmental endocrine disruptors represent one of the most significant threats to hormonal health. These chemicals interfere with hormone production, metabolism, or activity and are found in countless everyday products.
Kitchen & Food
- • Replace plastic containers with glass
- • Avoid heating food in plastic
- • Choose fresh/frozen over canned
- • Filter drinking water
- • Buy organic when possible
Personal Care
- • Read ingredient labels carefully
- • Avoid parabens and phthalates
- • Choose fragrance-free products
- • Use natural alternatives
- • Limit synthetic chemicals
Household
- • Natural cleaning products
- • HEPA air filtration
- • Low-VOC furnishings
- • Plants for air purification
- • Reduce EMF exposure
Gut Health and Hormone Balance Connection
The gut microbiome plays increasingly recognized roles in hormone metabolism and regulation. The estrobolome—gut bacteria capable of metabolizing estrogens—directly influences estrogen levels and activity.
Supporting Gut Health
- Probiotic Foods: Kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, yogurt
- Prebiotic Fibers: Garlic, onions, Jerusalem artichokes
- Gut-Healing Nutrients: L-glutamine, zinc, omega-3s
- Bone Broth: Collagen for intestinal barrier integrity
Avoiding Gut Disruptors
- Antibiotics: Only when necessary, follow with probiotics
- NSAIDs: Can damage intestinal barrier
- Processed Foods: Disrupt beneficial bacteria
- Chronic Stress: Affects gut-brain axis
11. Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to see results from hormone optimization?
Most people begin noticing improvements in energy, sleep, and mood within 2-4 weeks of implementing comprehensive hormone optimization strategies. However, significant changes in hormone levels and more substantial improvements typically require 3-6 months of consistent implementation.
- • 2-4 weeks: Initial improvements in energy, sleep quality, mood
- • 6-12 weeks: More stable energy, better stress tolerance, improved body composition
- • 3-6 months: Significant hormone level changes, substantial symptom relief
- • 6+ months: Full optimization and long-term benefits
Is hormone optimization safe for everyone?
Natural hormone optimization approaches are generally very safe for most people when implemented appropriately. However, certain groups should work with qualified healthcare providers:
- • Individuals with existing medical conditions (diabetes, heart disease, autoimmune disorders)
- • Those taking medications that may interact with supplements
- • People with severe hormonal imbalances requiring medical intervention
- • Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- • Individuals with a history of hormone-sensitive cancers
What’s the difference between hormone optimization and HRT?
The key differences lie in approach and philosophy:
Hormone Optimization
- • Supports natural hormone production
- • Addresses root causes
- • Systems-based approach
- • Lifestyle and nutrition focused
- • Minimal side effects
- • Long-term sustainable
Traditional HRT
- • Adds external hormones
- • Symptom management focus
- • Single hormone approach
- • Pharmaceutical intervention
- • Potential side effects
- • May create dependency
Can I optimize my hormones naturally without supplements?
Yes, many people can achieve significant hormone optimization through lifestyle factors alone, though supplements can accelerate and enhance results. The foundation always includes:
Essential Lifestyle Factors
- • Quality sleep (7-9 hours nightly)
- • Stress management and relaxation
- • Regular resistance training
- • Nutrient-dense whole foods diet
- • Toxin exposure reduction
- • Adequate sunlight and vitamin D
When Supplements Help
- • Correcting specific nutrient deficiencies
- • Supporting during times of high stress
- • Accelerating detoxification processes
- • Addressing genetic variations
- • Managing severe symptoms
- • Optimizing beyond basic needs
How often should I test my hormone levels?
Testing frequency depends on your current status and optimization goals:
- • Baseline Testing: Comprehensive panel before starting optimization
- • During Active Optimization: Every 3-6 months to track progress
- • Maintenance Phase: Annual testing once optimal levels achieved
- • Symptoms Return: Test immediately if symptoms worsen
- • Major Life Changes: Test during periods of high stress, illness, or life transitions
Remember that symptoms are often more important than lab values alone. Track how you feel alongside testing for the most complete picture.
Can hormone optimization help with weight loss?
Yes, hormone optimization can significantly support weight loss and body composition improvements by addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances that make weight loss difficult:
How Hormones Affect Weight
- • Insulin resistance: Promotes fat storage
- • Cortisol elevation: Increases belly fat
- • Thyroid dysfunction: Slows metabolism
- • Low testosterone: Reduces muscle mass
- • Estrogen dominance: Increases hip/thigh fat
Optimization Benefits
- • Improved insulin sensitivity
- • Better fat burning and metabolism
- • Preserved muscle mass during weight loss
- • Reduced cravings and appetite
- • More stable energy for exercise
12. Conclusion and Next Steps
Key Takeaways
Hormone optimization represents a comprehensive approach to supporting your body’s natural ability to produce, balance, and utilize hormones effectively. Unlike traditional hormone replacement therapy, optimization addresses root causes while supporting overall health and vitality.
Essential Principles for Success:
- Address Root Causes: Focus on underlying factors like stress, nutrition, sleep, and toxin exposure rather than just symptoms
- Systems Approach: Recognize that hormones work together as an interconnected network
- Lifestyle Foundation: Sleep, stress

